Load Balancing with API Management (APIM)
Load balancing is a fundamental aspect of scaling, crucial for optimizing performance, ensuring reliability, and maintaining scalability. API Management (APIM) has introduced an advanced load balancing feature specifically designed to address challenges related to token exhaustion and throttling, particularly in environments leveraging Open AI and similar high-demand services. This article provides a detailed examination of APIM’s load balancing capabilities, its background, and how to configure it effectively.
Background: Mitigating Token Exhaustion and Throttling
In high-traffic environments, such as those using Open AI, managing token exhaustion and throttling is essential to ensure smooth operation and even distribution of traffic across multiple instances.
APIM’s load balancing feature was developed to address these issues by distributing incoming traffic across multiple backend services. This approach helps prevent any single backend from becoming a bottleneck, thus reducing the risk of token exhaustion and minimizing the impact of throttling.
Key Use Cases for APIM’s Load Balancing Feature
-
Distributing Traffic Across Multiple Backends: APIM’s load balancing allows you to spread incoming requests across multiple backend services. This distribution is crucial for maintaining system stability, especially when backends have their own circuit breakers. By ensuring an even distribution of requests, load balancing helps prevent any one backend from being overwhelmed.
-
Facilitating Blue-Green Deployments: Blue-green deployment is a strategy for minimizing downtime during service upgrades. APIM’s load balancing simplifies this by enabling a smooth transition of traffic between old (blue) and new (green) versions of a service. This controlled shift helps ensure that updates are deployed with minimal disruption and allows for easy rollback if needed.
-
Scaling Across Multiple Regions: For organizations operating globally, scaling APIs across different regions is critical. APIM’s load balancing feature efficiently manages traffic across various geographical locations, ensuring consistent performance and responsiveness for users regardless of their location.
-
Managing Multiple Vendors: When working with multiple vendors offering similar services, load balancing can route traffic based on specific criteria. This capability ensures that requests are directed to the most suitable vendor, optimizing service quality and operational efficiency.
Load Balancing Strategies in APIM
APIM provides several load balancing strategies to cater to different traffic management needs. Each strategy can be configured with weights and priorities ranging from 1 to 100, allowing for fine-tuned control over traffic distribution:
- Round-Robin:
- Description: The round-robin strategy distributes incoming requests evenly across all available backends.
- Use Case: Ideal when all backends have similar performance capabilities. This method ensures that traffic is shared equally, providing a straightforward and equitable distribution of requests.
- Weighted:
- Description: The weighted strategy assigns a numerical weight to each backend, with values ranging from 1 to 100. Requests are then distributed based on these weights, allowing for proportional traffic allocation.
- Use Case: Useful when backends have varying capacities or performance levels. For example, if you have a high-capacity backend, you can assign it a higher weight to handle a larger share of the traffic. This is particularly useful during blue-green deployments or when integrating new services.
- Priority-Based:
- Description: In the priority-based strategy, backends are organized into priority groups, with each group having a priority value between 1 and 100. Requests are routed based on these priority levels, and within each group, traffic can be distributed evenly or according to assigned weights.
- Use Case: Effective for scenarios where specific backends need to handle traffic before others. This approach is beneficial for phased rollouts, where certain services should be prioritized based on operational needs or readiness.
Configuring Backend Pools
APIM allows up to 30 backends to be included in a single load balancing pool. This flexibility supports a range of backend configurations and traffic management strategies. Here’s how to configure backend pools effectively:
Scenario Overview
Assume you have two APIs:
- API A:
https://hemnttest/LBDemo/APIA - API B:
https://hemnttest/LBDemo/APIB
You need to configure load balancing such that 80% of the traffic is directed to API A and 20% to API B.
Steps to Configure Load Balancing
-
Create Backends for Each API
First, you need to create backend services for both APIs. This can be accomplished using Azure Management REST API. For simplicity, we will use identifiers for backend services as follows:
- Backend for API A:
backendLBA - Backend for API B:
backendLBB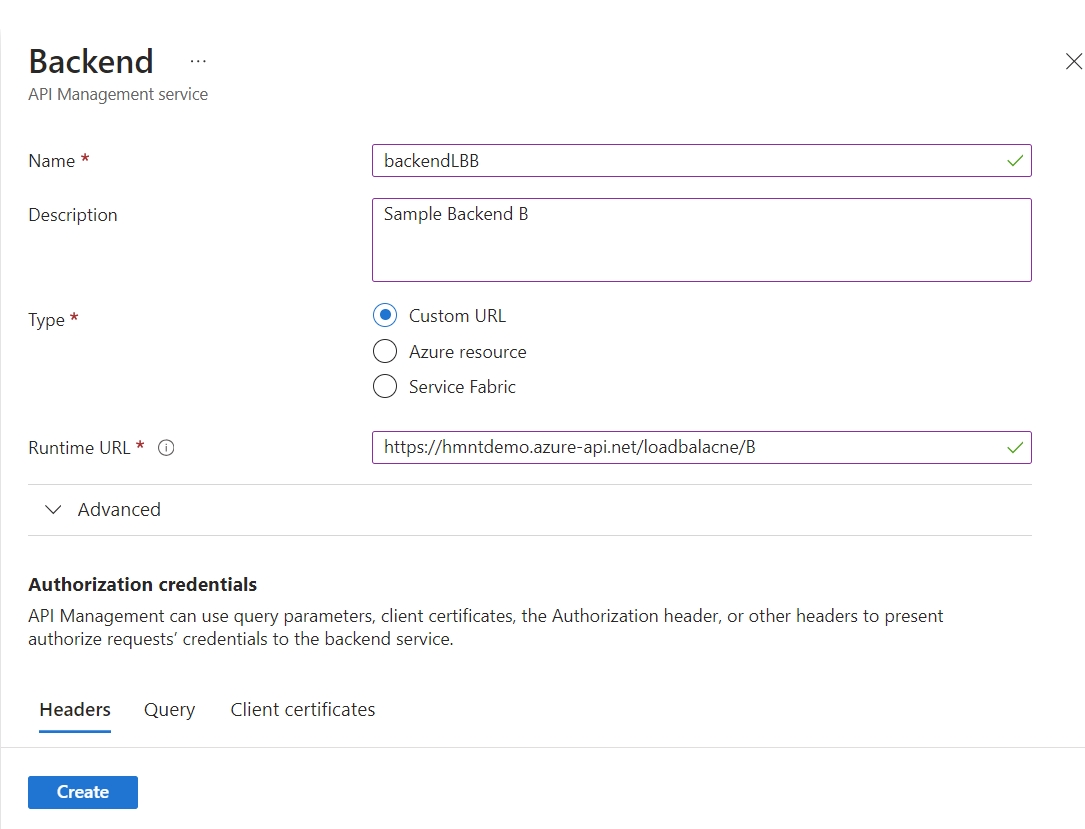
- Backend for API A:
-
Define the Backend Pool Using REST API
The backend pool configuration specifies how traffic is distributed among the backend services. We will use the Azure Management REST API to create this backend pool with weighted load balancing.
API Endpoint for Creating Backend Pool:
PUT https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/resourceGroups/{resourceGroupName}/providers/Microsoft.ApiManagement/service/{serviceName}/backends/{backendId}?api-version=2023-09-01-previewParameters:
- subscriptionId: Your Azure subscription ID (UUID format).
- resourceGroupName: The name of the resource group containing your API Management service.
- serviceName: The name of your API Management service.
- backendId: A unique identifier for the backend entity (this will be the backend Name).
- api-version: The API version to use for this request.
Authentication:
You must authenticate using Azure Active Directory OAuth2. You can obtain a bearer token using the following URL:
https://login.microsoftonline.com/common/oauth2/authorizedetailed steps to obtain a bearer token can be found at How to Retrieve a Bearer Token via API for Azure
Sample Request Body:
{ "properties": { "type": "Pool", "description": "Demo of weighted load balancing using API management", "pool": { "services": [ { "id": "/backends/backendLBA", "priority": 1, "weight": 80 }, { "id": "/backends/backendLBB", "priority": 1, "weight": 20 } ] } } }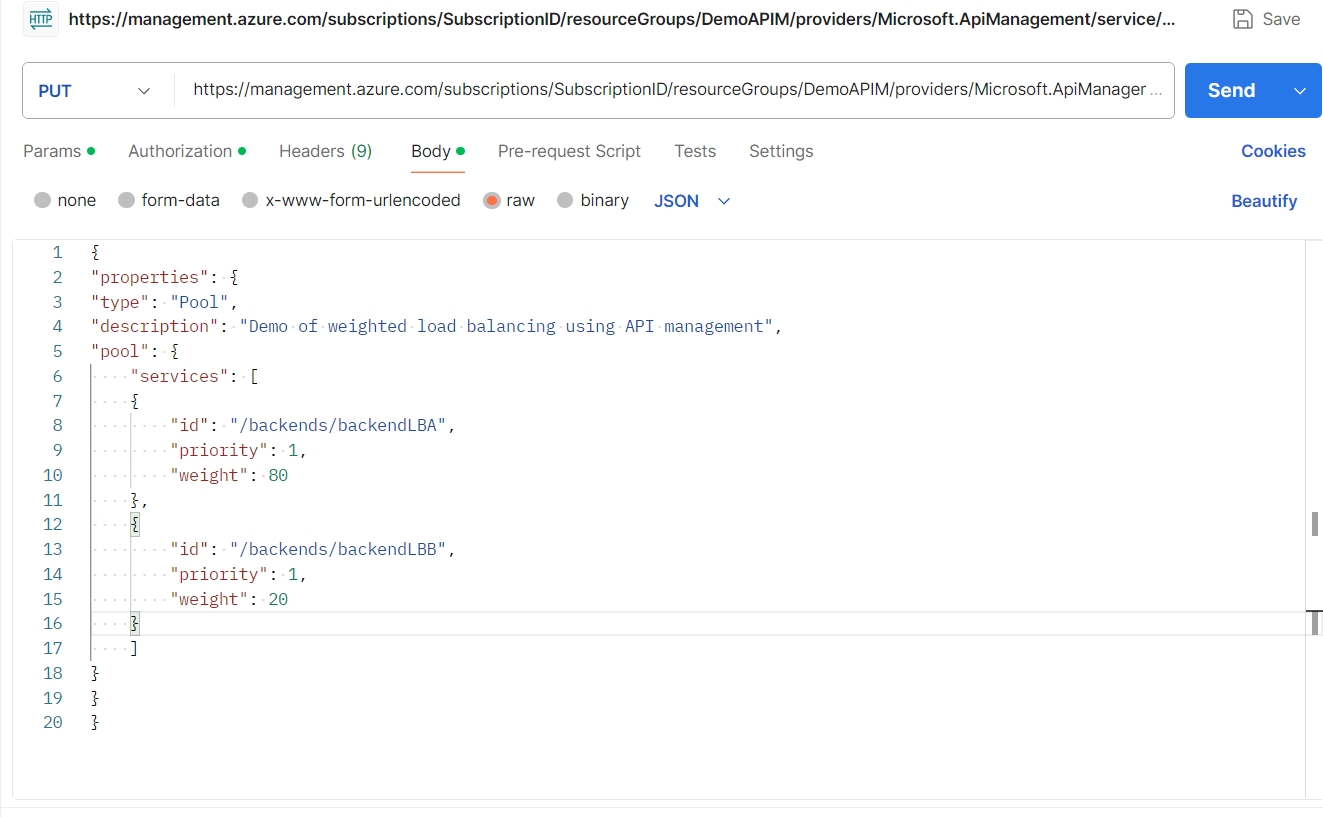
### Key Parameters for Backend Service Configuration ####
- id: Backend Service Identifier
- Purpose: The
idfield uniquely identifies a backend service within your API Management service. This ID is essential for referencing the specific backend you wish to configure.- Format: The value of
idtypically follows the format"/backends/{serviceBackendName}". Here,{serviceBackendName}is a placeholder for the actual name you assigned to your backend service during its creation.
- Format: The value of
- Example: If you named your backend service for API A as
backendLBA, then theidfor this backend would be"/backends/backendLBA".
- Purpose: The
- priority: Service Priority Level
- *
priorityfield determines the order in which backend services are considered when distributing traffic. This is useful if you have multiple backends and want to control which services are favored under certain conditions.
- *
-
weight: Traffic Distribution Weight - weight field specifies the proportion of traffic that should be directed to a particular backend service. It helps in balancing the load among multiple services based on the assigned weights.
Expected Response: On successful execution, you should receive a
201 Createdresponse code indicating that the backend pool has been created. We should be able to see the backend created in Azure Portal
Update API Configuration to Use the Load Balancer
After setting up the backend pool, update your API configuration to use the newly created load balancer. This involves adding the following Inbound policy to your API configuration:
<set-backend-service backend-id="LBBackend" />
Test the Configuration
With the load balancer configured, you can now test the traffic distribution. Ensure that 80% of the requests are directed to API A and 20% to API B. This can be done using API testing tools or by sending a high volume of requests and observing the traffic distribution.
View Configuration
Call the API with a GET request.
GET https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/resourceGroups/{resourceGroupName}/providers/Microsoft.ApiManagement/service/{serviceName}/backends/{backendId}?api-version=2023-09-01-preview
Update Configuration
Call the API with a PUT request. Upon a successful update, a 200 OK status code will be received instead of a 201 Created status code.
APIM’s load balancing feature is a powerful tool for optimizing traffic management and addressing issues such as token exhaustion, throttling, and slow responses. By utilizing strategies like round-robin, weighted, and priority-based distribution, and configuring weights and priorities from 1 to 100, you can enhance the performance, reliability, and scalability of your API infrastructure. Effective configuration and management of backend pools will help ensure that your APIs remain resilient and efficient, meeting the demands of both current and future traffic.